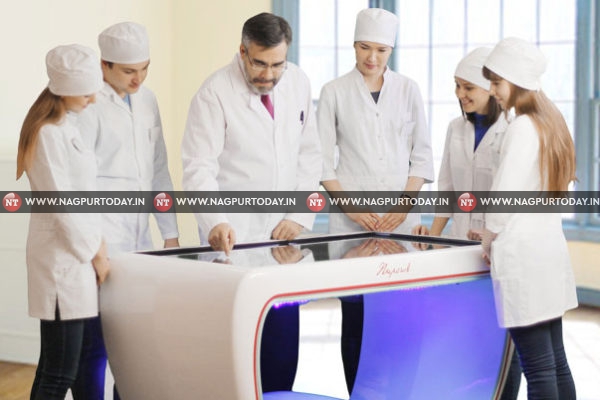
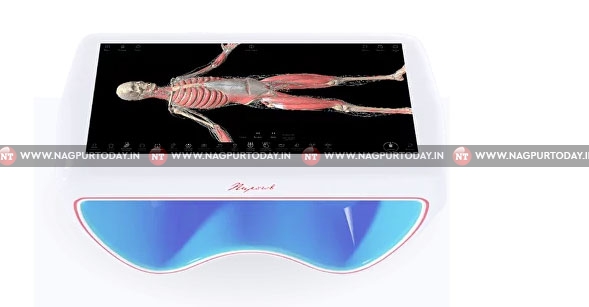
The field of medical education has witnessed significant transformations with the advent of digital technologies. One of the most groundbreaking advancements is the development of the Digital Dissection Table — an innovative tool that enhances the learning and teaching of human anatomy. This article explores the concept, evolution, and impact of digital dissection tables, highlighting popular virtual models, including the renowned Pirogov Table. By examining their benefits, limitations, and future prospects, we aim to elucidate the pivotal role these digital tools play in contemporary medical training and practice.
2. History of Anatomical Tables
Traditional Methods and Physical Tables
Anatomy education has long relied on cadaveric dissections, utilizing physical anatomical tables for hands-on learning. These traditional methods, while invaluable for providing tactile experience and real-life anatomical variations, come with limitations such as the high cost of maintenance, ethical concerns, and limited accessibility.
Development of Anatomical Models
To address some of these challenges, educators introduced anatomical models and textbooks, which offered standardized representations of human anatomy. However, these models lacked the interactivity and dynamic visualization capabilities necessary for comprehensive understanding.
Transition to Digital Technologies
The digital revolution brought about a paradigm shift in anatomical education. Advances in computer graphics, virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and 3D modeling paved the way for the creation of digital dissection tables. These technologies offer interactive, scalable, and easily updatable platforms that enhance the learning experience beyond the capabilities of traditional methods.
3. Digital Dissection Tables: An Overview
Definition and Components
A Digital Dissection Table is an interactive, computer-based platform that simulates human anatomy for educational and clinical purposes. Key components typically include high-resolution touchscreens, 3D anatomical models, VR/AR integration, and user-friendly interfaces that allow manipulation and exploration of anatomical structures.
Technologies Employed
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): These technologies provide immersive experiences, enabling users to interact with 3D anatomical models in a simulated environment.
3D Modeling and Animation: High-fidelity models allow for detailed examination of anatomical structures from various angles and perspectives.
Interactive Interfaces: Touchscreen and gesture-based controls facilitate intuitive navigation and manipulation of anatomical data.
Advantages Over Traditional Methods
Digital dissection tables offer numerous benefits, including:
Interactivity: Users can engage with anatomical structures dynamically, enhancing retention and understanding.
Accessibility: Digital models can be accessed remotely, broadening the reach of medical education.
Customization: Content can be easily updated and tailored to specific educational needs.
Safety and Ethical Compliance: Eliminates the need for cadaveric specimens, addressing ethical and logistical concerns.
4. Popular Virtual Anatomical Tables
4.1. Pirogov Table
Historical Overview and Creation
Pirogov anatomy table (https://pirogov-anatomy.com) pays homage to Nikolai Pirogov, a pioneer in abdominal surgery and anatomical education. Developed to honor his contributions, this digital table integrates historical insights with modern technology, offering a comprehensive tool for both education and clinical practice.
Features and Functional Capabilities
Detailed 3D Models: High-precision anatomical structures with layers that can be peeled back to reveal underlying systems.
Interactive Simulations: Enables users to perform virtual dissections, simulating surgical procedures.
Educational Modules: Includes quizzes, annotations, and guided tutorials based on Pirogov’s methodologies.
Impact on Anatomical Education and Clinical Practice
The Pirogov Table has revolutionized anatomy teaching by providing a deeply interactive platform that enhances student engagement and comprehension. In clinical settings, it assists surgeons in planning complex procedures, ensuring a higher degree of precision and preparedness.
4.2. Other Leading Digital Anatomical Tables
Anatomage Table
Description and Functions: The Anatomage Table is one of the most widely recognized digital dissection tables. It features a large, interactive touchscreen that allows for detailed exploration of human anatomy through cadaveric scans and 3D models.
Educational Applications: Used extensively in medical schools worldwide, it facilitates interactive lectures, self-paced learning, and collaborative study sessions.
BodyViz
Technological Features: BodyViz incorporates advanced image processing and VR capabilities, offering highly detailed and customizable anatomical visualizations.
Clinical Uses: Primarily utilized in surgical planning, BodyViz assists surgeons in visualizing patient-specific anatomy, enhancing precision in complex procedures.
Skeleton Model Virtual
Unique Capabilities: Skeleton Model Virtual focuses on the skeletal system, providing intricate 3D models that can be dissected and examined layer by layer.
User Feedback: Praised for its intuitive interface and detailed representations, it is favored by both educators and students for its ease of use and comprehensive anatomical coverage.
5. Applications of Digital Anatomical Tables
Educational Programs and Medical Training
Digital dissection tables are integral to modern medical curricula, offering interactive and engaging tools for anatomy education. They support diverse learning styles and provide opportunities for repeated practice without the constraints of physical specimens.
Surgical Planning and Simulations
Surgeons utilize these digital tools to plan and rehearse operations, reducing the risk of errors and improving surgical outcomes. Virtual simulations allow for the exploration of different approaches and techniques in a risk-free environment.
Research and Development
Researchers leverage digital dissection tables to study anatomical variations, develop new surgical techniques, and advance biomedical research. The ability to manipulate and analyze detailed anatomical data accelerates innovation and discovery.
Interdisciplinary Uses
Beyond medicine, digital anatomical tables find applications in fields such as biomedical engineering, where they aid in the design of medical devices, and in bioinformatics, facilitating the integration of anatomical data with computational models.
6. Advantages and Limitations of Digital Anatomical Tables
Advantages
Interactivity: Enhances engagement and depth of learning through hands-on virtual interactions.
Accessibility: Offers remote and flexible access to anatomical resources, democratizing education.
Upgradability: Facilitates the incorporation of the latest anatomical discoveries and technological advancements.
Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces the need for physical specimens, lowering educational expenses over time.
Limitations
Cost: High initial investment may be prohibitive for some institutions.
Technical Expertise: Requires training for effective use and maintenance.
Technical Issues: Susceptible to software glitches, hardware malfunctions, and the need for regular updates.
Limited Tactile Feedback: Unlike physical dissections, digital tables cannot replicate the tactile sensations of manipulating real tissues.
Comparison with Traditional Methods
While digital dissection tables offer numerous advantages in terms of flexibility and interactivity, they complement rather than completely replace traditional dissection methods. A hybrid approach, leveraging both digital and physical tools, often yields the best educational outcomes.
7. The Future of Digital Anatomical Tables
Technological Advancements
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning will further enhance the capabilities of digital dissection tables, enabling personalized learning experiences and predictive analytics for surgical planning.
Impact on Medical Education and Practice
As digital tools become more sophisticated, they will become indispensable in medical education, offering increasingly realistic simulations and comprehensive anatomical insights. This evolution will lead to more proficient and well-prepared healthcare professionals.
Integration with Other Digital Medical Systems
Future developments will see seamless integration with electronic health records (EHRs), telemedicine platforms, and other digital health systems, fostering a cohesive and efficient healthcare ecosystem.
8. Conclusion
Digital dissection tables represent a significant advancement in medical education and clinical practice, offering interactive, accessible, and customizable tools that enhance the understanding of human anatomy. The Pirogov Table and other leading virtual models exemplify the transformative potential of these technologies. While challenges such as cost and technical limitations persist, the benefits they provide in terms of educational efficacy and clinical precision are undeniable. As technology continues to evolve, digital dissection tables will undoubtedly play an increasingly central role in shaping the future of medical training and healthcare delivery.